半導體 (Semiconductor)
解決方案與軟體
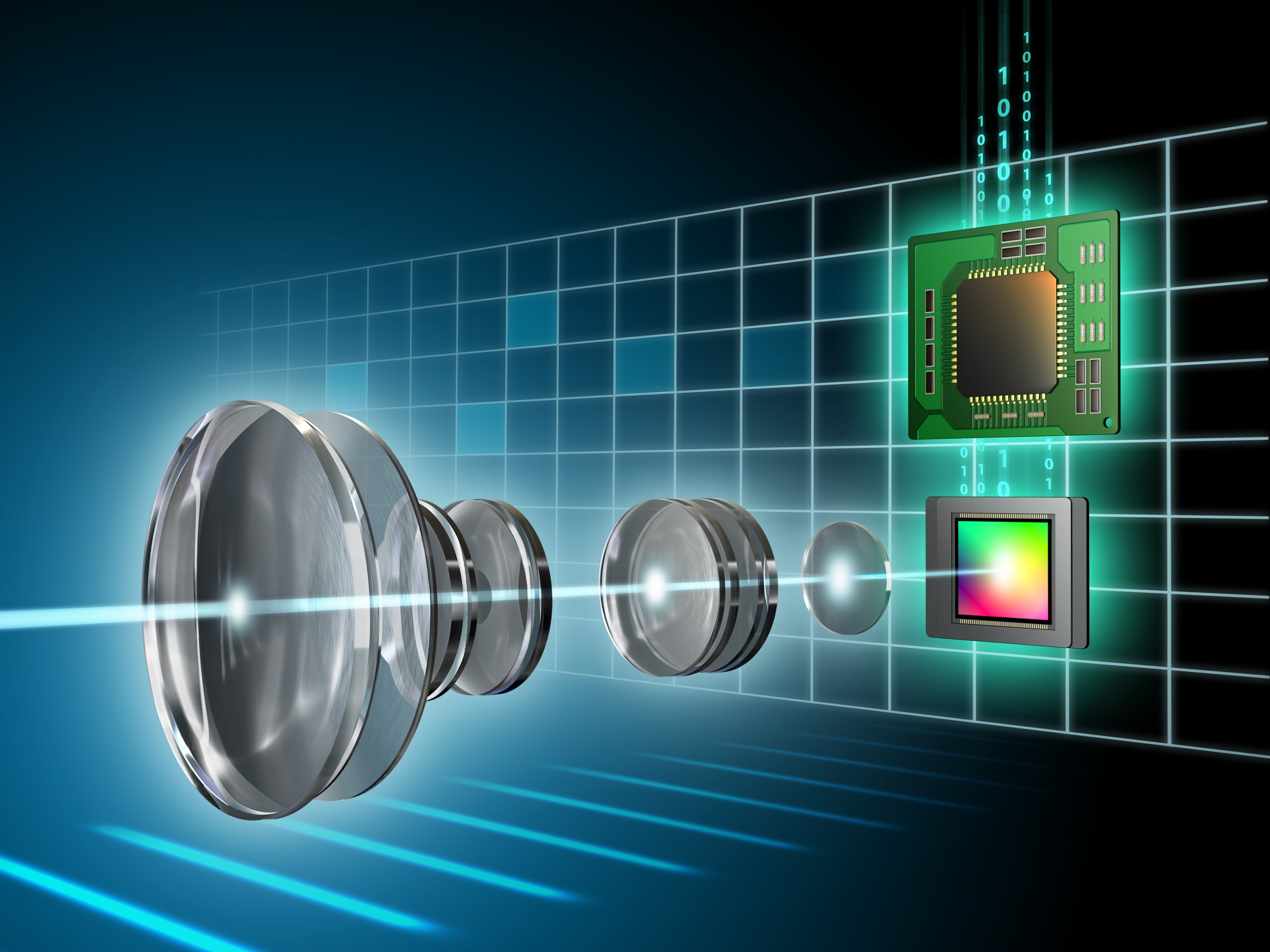
CMOS 影像感測器
基於 CMOS 的影像感測器 (CIS) 作為攝影機廣泛應用於各種終端市場,例如智慧型手機、汽車、安全、擴增實境/虛擬實境 (AR/VR)、工業視覺和醫療系統。 CMOS 影像感測器在稱為光電二極體的裝置中將傳入的光能或光子轉換為電訊號。 每部智慧型手機都有兩到六個攝像頭,而汽車則有多個外部和一些內部車內視覺系統。
基於事件的感測僅在視野發生變化時捕捉訊號。 影像捕捉、影像分析和機器學習的結合,推動了從攝影成像到訊息成像的應用,為基於人工智慧的智慧型攝像頭拓展了道路。
智慧型手機和相機製造商專注於改善影像感測器的解析度、靈敏度和速度。 這些可以透過像素大小/間距的微縮、新型元件結構,如像素堆疊或 3D 像素,或新型光電二極體管材料來加以實現。 除了像素縮放之外,其他重要屬性是高動態範圍,它是指相機或感測器在高光和低光條件下工作的能力以及暗電流,它代表設備中的雜訊水平。
應用材料公司憑藉我們在蝕刻、外延、處理、金屬沉積、化學機械平坦化 (CMP)和注入領域的廣泛產品組合來滿足這些要求。透過提供全面的設備和 IMS™(整合材料解決方案® )™組合,應用材料公司還能夠開發和製造下一代 CIS 設備。